Ethnic assertion? Autonomy offensive? Liberation movement? Sankarshan Thakur travels to Kathmandu and the Tarai to get a sense of the ominous new rumblings in the neighbourhood.
An alarming, and unheralded, civil war is spiralling to intensity along the sweep of India’s open frontier with Nepal. Allowed to fester, it could torpedo the fragile peace plan taking shape in Kathmandu, unleash a cascade of refugees into Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, and present New Delhi the anathema of a un mission digging into its backyard.
The erupted eye of this storm is an anarchic movement for self-determination by the plains people of Nepal. There are parallel armed insurgencies gunning for liberation, rival political groups seeking varied degrees of autonomy, and an establishment party from the region desperate to put out the fires and regain a measure of credibility in its home borough.
Madheshi ire has long been on slow-burn for reasons of institutionalised political, economic and social discrimination at the hands of a Pahadi (hill people) hegemony that has held sway over Nepali affairs for centuries — under the Shah kings, under long spells of Rana dictatorship, under democratic interregnums as well. This January, a small incident close to the border with India became the flashpoint of a volatile upsurge that both Kathmandu and New Delhi will have to contend with.
An armed Maoist patrol clashed with activists of the Madheshi Janjagaran Forum (MJF), currently the best-known face of the Madheshi rebellion, in a small town called Lahan. Ramesh Mahato, an MJF apparatchik, was shot dead. The next day, the tempers still high, Maoists snatched Mahato’s body from MJF custody and cremated it.
The chain of violence Lahan unleashed is yet to be stilled. Pitched battles have been fought between security forces and Madheshi rights activists. Government establishments have been attacked and symbols of Pahadi dominance such as the constitution, photographs of the king and the Nepali topi publicly burnt. Slogans of a new nationalism have flowered across the region. In many pockets, nervous Pahadi residents have begun to contemplate flight to the hills — properties are being put on sale, women and children are being shifted to Kathmandu, businesses are being shut. It isn’t a Pahadi exodus yet, but it could become one. “We are grabbing their illegally captured lands and handing them to poor Madheshi workers,” claims an insurgent commander in Janakpur in eastern Madhesh, “We don’t want them here and they know it.” Told that this could lead to a backlash against Madheshis in the hills, an aide retorts, “Good, that’s what we want, Pahadis in the hills and Madheshis in Madhesh.”
Scare has its reasons. More than a hundred people have been killed in street protests and organised intra-group massacres; last week alone, one or the other insurgent group struck daily, claiming 18 lives. West to east, Madhesh has remained paralysed, bandh-bound or curfew-ridden. Swept into the whirl of heated opportunity, political and insurgent groups have stoked the embers of Madheshi grievance into many flaring fires. A top un observer in Kathmandu says the situation could tip “overnight” into a perilous flashpoint. A senior Indian diplomat in the Kathmandu mission is more blunt about boil and its implications. “Take serious note now,” he says, calling both Nepal and his home country to attention, “Potentially things are very dangerous, you could have all of UP and Bihar battling fire tomorrow and the heat will reach Parliament. This movement has reared its head dramatically.”
Madhesh is an entity (see box) most Indians aren’t even aware of and Nepalis are only grudgingly beginning to recognise. There is good reason to be cautious about over-reading the signs of alarm, but it could be fatal to underestimate the implications of a suppressed nationalism exploding into protracted and violent strife through the belt. “Madheshi sentiment is running impatient,” warns Dhirendra Premarshi, a Madheshi radio artist, who keeps a firm finger on the Tarai pulse, “The foundations of Madheshi secession are probably being built, and they are being built by the Kathmandu Pahadis, who will not even recognise Madheshis as humans. The only problem is Madhesh has a crisis of leadership, there are too many people trying out too many different things to keep pace with the public mood.”
For many Madheshi leaders, this is a now-or-never battle. Elections for a new Constituent Assembly (ca) are scheduled for November, and Madheshi political groups see it as their last chance to grab their rightful share of power and consequent benefits. Rocked by the vehement powderflash in the plains, Prime Minister GP Koirala scrambled to grant placatory concessions in February — the promise of a federal state, more government jobs and nearly half the seats in the ca to Madhesh. But that has done little to assuage anger or aspiration. “Koirala made it sound as if he was a feudal granting us a favour,” says Vijaykant Karan, a Kathmandu-based political scientist and Madheshi activist. “And how can we be sure we will get the little he has promised? Madheshis don’t want to plead anymore, they will snatch what they think is theirs, they want to end centuries of slavery.”
The MJF’s manifesto is a scorching indictment of Kathmandu. “Madhesh is an internal colony of the ruling hill people. Madheshis have been subjected to extreme national oppression, poverty, exploitation and discrimination. They are politically, economically, socially and culturally depressed. They have been strategically forced to migrate to India. Their landholdings have been confiscated, their languages have been choked…” On the ground, anti-Pahadi feeling can find more visceral and graphic expression. “Saala log humlog ko dhoti-muji bolta hai aur apne hi jameen par daba ke rakha hai. Pahadi raj ab nahin chalega,” a Madheshi labourer in Janakpur tells us, “yahan Pahadi police aur Pahadi afsar kahe rahega, humko apna log chahiye. Yahi ladai hai.” (They refer to us as dhoti-wearers and pubic hair, they have suppressed us in our own country. Why must we live under Pahadi police and Pahadi officials? That can’t continue, that is the fight now.)
Kanak Dixit, journalist and Kathmandu intellectual both liberal and engaged, agrees the anger has basis. “Madheshis have never been made to feel part of Nepal, it is true,” he says. “The psychology of this country is a hill psychology, they always look down upon the plains, to the extent of there being an element of racism. Madheshis have had many issues with the Pahadis, although I must say everybody was surprised by the intensity of the outburst. The state will have to respond with sensitivity and a genuine desire to redress grievances, else this could spread.”
Madheshi protagonists, from the moderate MJF leader Upendra Yadav (see interview) to even mainstream actors like Ajay Chaurasia, a Nepali Congress MP, aren’t terribly sure of a transformation in the Pahadi mindset, even though they might hope and pray for it. “They are too used to being patronising,” Chaurasia says. “If they cannot learn now, there is bigger trouble coming, it is already too late.” Leaders such as him perhaps already sense the ground slipping underneath as Madheshi aspirations turn more radical and tug the goals of the movement beyond mere autonomy. And the MJF leadership, holding talks with the interim government in Kathmandu, might have good reason to sense they are losing support on the ground because they might be seen as people who jumped too quickly to compromise, or worse, as collaborators. “The issue is not what they will give or not give in the Constituent Assembly,” rails Rajan Mukti, a young underground militant who heads the operations of the Janatantrik Tarai Mukti Morcha (JTMM-Jwala) in Dhanusha district. “The issue is who are they to give? One Pahadi dies and he is officially named a martyr by the government, dozens of Madheshis die and there is not even a word on them. That is the issue, this is a battle for self-respect and in Nepal we will never get that, everybody knows.” Rival JTMM leader Jaikrishna Goit is more ruthless on moderates (see interview). “The Pahadis will manipulate and cheat them, they know it, this is nothing that can be sorted out through talks and compromise, this is a struggle for Madheshi self-determination, we are not looking for crumbs.”
For centuries, Madheshis complained about not being heard by the Pahadis. Now, many of them are refusing to communicate. The widespread sense that there lies little merit in trying to negotiate a deal with leaders in Kathmandu could become a major roadblock to solutions. Even the Maoist chief Prachanda, who first spoke of addressing Madheshi self-rule during his days in the jungles, is now seen as part of the Pahadi (and therefore anti-Madheshi) clique. It is not uncommon in Madhesh to hear Prachanda being clubbed with the bourgeois Pahadi establishment — Nepal is ruled by four Pahadi Bahuns (Brahmins, traditionally the ruling elite along with Chhetris, or Rajputs) — GP Koirala, Madhav Nepal, Prachanda and Baburam Bhattarai. That rankles Maoists, but they concede they made mistakes. “We slipped up on Madhesh,” admits Anil Shreshtha, party secretary of Parsa, a central Madhesh district, “When we were negotiating our entry into the interim government, we did not talk Madhesh.” Maoists are eager to pledge corrections, but Madheshis appear to have convinced themselves their failure was not an ideological lapse, it was deliberate because somewhere they too believe in Pahadi hegemony. Much of the popular Madheshi anger today is directed at Maoists; Lahan was a symptom of it.
Most of Madhesh is a doppelganger of what lies immediately south — UP and Bihar. A pitifully impoverished and under-developed rural stretch, riven by feudalism and other forms of social oppression. It lacks for good roads, power, water, healthcare, education, administration. You could land in Simra near Raxaul upon a 20-minute air-hop from Kathmandu and feel you have arrived to the worst Bihar can showcase. What’s different in Madhesh, though, is that it has seen none of India’s affirmative processes of democracy at work — no redressal of regional aspiration, no positive discrimination for the underprivileged, no sense of a political leadership that will speak for them and get purchase. For the better part, Madheshis have been subjects, not citizens. And during the few phases of democracy, they’ve felt defrauded by the Pahadis who rule Kathmandu. “We don’t have a sense of democracy,” says Chandrakishore Jha, a Madheshi editor, based in Birgunj. “How could we? The Pahadis imposed the slogan of ek des, ek bhes, ek bhasa (one nation, one dress, one language), everything about the Madheshis got crushed. All the chaos breaking out is a result of that, and the problem is nobody is sure where we are headed.”
Jha probably typifies the confounded confusion of the Madheshi mind. All around, there is a rising clamour for self-rule, but, equally, there is the absence of clarity on critical issues. What’s to be the framework of self-rule? Independence? Autonomy within Nepal? A federal self-government that gives Madheshis the right to conduct their affairs as well as a stake in power in Kathmandu? Their aspirations have spawned a hydra of militancies — too many leaders offering too many routes to salvation. “It is a movement that evolves almost daily,” says Pradeep Giri, one of Nepal’s seniormost politicians, a Pahadi who has made his home in Madhesh, “The consciousness of the Madheshi is changing, probably it is becoming more militant. It needs a leader to channel all that, but there is vacuum. But that does not mean Kathmandu can continue taking it for granted.” For the moment, perhaps, Madheshis are merely happy they have shaken the Pahadis’ many assumptions of divine right to rule.
THE THEATRE
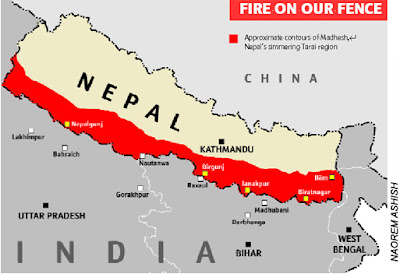
WHAT IS MADHESH?
Nepal's southern-most strip of flat land, an 885km stretch contiguous to UP, Bihar and West Bengal. Large parts are still covered with thick malarial jungles, but this strip is also home to nearly half of Nepal's 27 million population. Also known as the Tarai, Madhesh is a recent nomenclature symbolising the region's new-found will for political self-determination.
WHY IS IT ON THE BOIL?
Because the majority plains people of Madhesh feel chronically discriminated against by the Pahadis who have always controlled power in Kathmandu. They had to fight for decades to obtain citizenship. The main Madheshi languages — Maithili, Bhojpuri, Awadhi, Tharu — are not recognised. They occupy less than 12 percent jobs in key sectors and almost none in the top bureaucracy, police or army. They have little political voice. They believe they are an internal colony of Pahadi Nepalis.
WHY SHOULD INDIA BE CONCERNED?
Greater Madheshi turmoil could unleash a huge refugee influx into UP, Bihar and parts of West Bengal. There is already an active insurgency in the region; many armed groups work out of the Indian side. Culturally and socio-economically, Madheshis mirror UP and Bihar. Besides, people maintain cross-border social and family ties. If unrest builds, India will be forced to intervene. Strategically, trouble in Madhesh could bring international agencies such as the un close on India’s borders, something New Delhi is loath to accept.
THE DRAMATIS PERSONAE
Nepal Sadbhavana Party (ANANDI)
The Tarai’s traditional party, has championed regional issues. Currently lacks for ground credibility because it is part of the interim government and is seen as having been sold out to the Pahadi political establishment. Madheshi Janjagaran ForumA civil society group brought to the fore after the violence earlier this year. Stops short of secession but seeks autonomy and is currently in talks with the interim government. Has brand-recognition across Madhesh but is still trying to build an organisational base.
Janatantrik Tarai Mukti Morcha (GOIT)
Led by former Maoist Jaikrishna Goit, the JTMM(G) is fighting an armed struggle for liberation. Stridently secessionist, cadre strength is difficult to estimate, but could run into a few thousands. Not well equipped, constantly looking for arms. Although not a stated aim, they are seeking a Pahadi exodus as a prelude to independence.
Janatantrik Tarai Mukti Morcha (JWALA)
A splinter faction of the JTMM(G), it has carried out most of the violence in Madhesh. Jwala, in his 40s, is more energetic than former mentor Goit, and is fast building a cadre-base in the eastern and mid-eastern Tarai. Is committed to independence, although not as ideologically grounded as Goit. Denies allegations of running a motley criminal outfit, sees himself as a serious claimant to Madheshi leadership.
Source: Tehelka, July 7, 2007



